As previously discussed in this newsletter, advances in artificial intelligence have had a massive impact on the world of digital marketing. Everything from content creation of data analysis have been completely revolutionized by AI, making it a crucial technology to understand for anyone looking to start a career in digital marketing. Advances in AI have also led to significant changes in how marketers use social media channels, enabling them to take advantage of the huge volumes of data that social media channels generate on a daily basis through a practice known as social listening. With that in mind, in this instalment of Mujo’s newsletter, we’ll discuss the importance of social listening, and provide some practical ways that digital marketing instructors can help their students better understand this crucial new practice.
What is Social Listening?
Social listening, also known as social media listening is the process by which you analyze and track conversation across social media platforms, capturing mentions of your brand, products, competitors, and industry with the use of advanced AI technologies. This process provides critical insights into your audience’s perceptions and feedback, helping you understand their needs, preferences, and sentiments more deeply. By monitoring these online discussions, you can identify emerging trends, address potential issues promptly, and refine your marketing strategies to better engage with your audience and stay ahead of the competition.
With that in mind, social listening may seem similar to social monitoring, or the practice of monitoring and replying to engagements on a brand’s social media platform. But where social monitoring is focused on narrow, individual interactions, social listening is focused on tracking conversations related to a given business in the aggregate. It does not seek to respond to individual brand mentions, but rather aims to collect and analyze every relevant mention across all social media channels. This kind of data can help businesses make informed decisions about future campaigns and other marketing efforts.
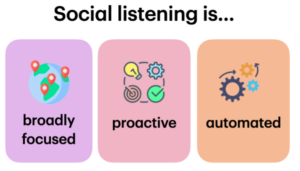
Social listening can be further distinguished from social monitoring based on three distinct characteristics.
Broad Focus
One of the defining characteristics of social listening is that it is broad in focus. Effective social listening involves taking a wide view of all ongoing conversations about a brand or related topics. Social listening tools allow marketers to pull data from across the internet and compile it into a meaningful set of insights. For instance, a marketer working for a vegan protein business may use a social listening tool to discover that people interested in vegan protein are also discussing vegan recipes that are easy to prepare. With this information, the marketer could develop a content marketing campaign that explores how the business’s protein could be used in various recipes.
Proactive
Where social monitoring is about reacting to customer comments, social listening is about proactively searching for opportunities. Marketers can use data collected by social listening tools to find and connect with new audiences. For instance, a marketer might use a social listening tool to discover that people in a business’s target audience are also fans of a micro-influencer who creates content in the same niche as the business. The marketer can use this information to reach out to this influencer and develop an influencer campaign to build a stronger relationship to these customers.
Automated
Where social monitoring requires careful attention to each individual interaction, social media listening deals with volumes of data that would be impossible to sort manually. Social listening makes use of a unique set of tools that automate the process of scouring the internet looking for particular terms and analyzing the resulting data into manageable insights. Importantly, though, this does not mean that social listening is easy: As with all automation tools, their output is only as useful as the information that marketers choose to put into them.
For digital marketing educators, the best way to introduce students to social listening is by examining the social listening features and benefits offered on popular social media management platforms. For instance, popular social management platform Hootsuite provides marketers with social listening tools through Hootsuite Streams. Students can be tasked with exploring Hootsuite’s documentation on social listening to learn more about the various features that they offer and how marketers can use them most effectively. Additionally, Mujo’s Influencer Marketing Fundamentals textbook provides extensive coverage and practical activities for introducing digital marketing students to a range of social media management and social listening tools.
How Does Social Listening Work?
While every social listening tool will have its own unique features and workflow, they tend to make use of keywords to track relevant conversations. Keywords are terms or short phrases used in a wide range of digital marketing practices, such as SEO and PPC advertising. In the context of social listening, digital marketers can use keywords to identify the topics or terms they want to monitor. Most commonly, this would include keywords like the business’s name or slogan, but can also include keywords related to the business, such as their competitors’ names or terms related to their industry or niche.
When engaging in social listening, marketers can track a range of keywords, including:
Brand keywords: Brand keywords are any terms directly associated with a given business or its products. These are the most crucial keywords for brands to use in social listening efforts, as they will help businesses track mentions and conversations that are directly related to their brand. For instance, a brand like Apple might track the brand keywords “Apple” and “iPhone” to learn more about what people are saying about their brand on social media.
Competitor Keywords: While businesses may be most interested in conversations about their own brand, it can also be useful to learn more about a business’s key competitors. This can help businesses identify potential pain points that a competitor’s customer may be experiencing and help them better position themselves within a given market. For instance, Apple may track other personal computer manufacturers like HP and Dell to learn more about their competitors’ customers.
Campaign Keywords: Campaign keywords are terms related to an ongoing marketing campaign. These terms help marketers track the impact that their campaigns are having on their audience. Campaign keywords might include the name of a campaign, or key phrases or slogans used in a campaign that audiences may pick up on. For example, Apple may track a phrase like “spatial computing” to learn how social media users are responding to the marketing campaign for their new Vision Pro headsets.
Industry Keywords: Industry keywords include terms or phrases that are connected to a business’s niche or industry. While these terms are only indirectly related to a given business, they can provide marketers with key insights into the topics being discussed within an industry. For example, Apple might track terms like “smart watch” or “virtual reality” to learn more about how social media users feel about these topics.
For educators, a great way to help digital marketing students explore keywords is to task them with choosing a local business and having them develop a list of keywords in the various categories discussed above. This kind of practical activity can help give students useful insight into how to work with social listening tools and prepare them for a successful career in the field of digital marketing.








 by
by